Arthritis
- ‘Arthr’ means joint
- ‘Itis’ stands for inflammation
- The term ‘Arthritis’ therefore means inflammation of the joint
- Causes swelling, pain, limitation of motion and, often, significant damage to the joints of our body
Osteoarthritis
- OA is the most common form of joint disease in humans and is a leading cause of disability among the elderly
How common is OA?
- Osteoarthritis is the most typical joint dysfunction, one of the most popular chronic diseases in the older people, and a primary reason of disability
- Approximately 50% of people > 70 years have some form of Osteoarthritis
- 80% of the patients with OA have some degree of limitation of movement, and 25% can not perform their major daily activities
- Prevalence in men >women below 50 yrs
- Above 50 yrs women affected > men
Risk Factors
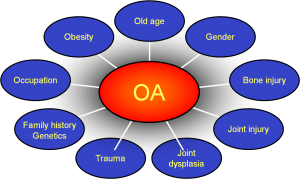
- Modifiable
- Excess body mass (especially knee OA)
- Physical inactivity
- Joint injury (sports, work, trauma)
- Occupation (due to excessive mechanical stress: hard labor, heavy lifting, knee bending, repetitive motion)
- Non-modifiable
- Gender (women higher risk)
- Age (increases with age and levels around age 80)
- Race (Chinese, Jamaican blacks, South African blacks, and Asian Indians have a lower incidence of Osteoarthritis)
- Genetics
Pathophysiology
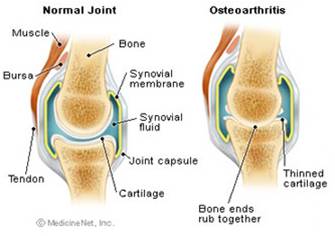
Osteoarthritis (OA) is disorder of joints in our body characterized by an imbalance between the synthesis and degradation of the joint cartilage, leading to the classic pathologic changes of wearing away and progressive destruction of cartilage
Osteoarthritis Joint
Signs & Symptoms
- The clinical features are gradual in onset
- Pain in joints (At first intermittent, provoked by joint use & relieved by rest, later – Persistent with Nocturnal aching )
- Stiffness in joints (morning stiffness 30 minutes)
- Night time pain
- Movement limitation
- Associated muscle wasting
- Bone deformity
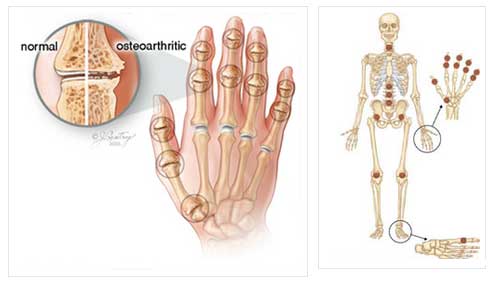
Joints affected in OA
Although osteoarthritis can occur in any joint, most often it affects the hands, knees, hips, and spine (either at the neck or lower back)
Diagnosis
- Detailed Clinical history
- Patient Examination
- Radiological examination
X-Ray features of OA
Aims of Treatment
- Relieve pain and associated symptoms
- Relieve stiffness & swelling
- Minimize or improve disability
- Maintain function of the joint and quality of life
Treatment Options
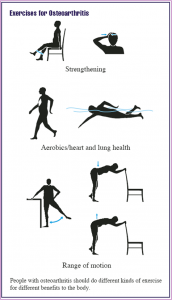
Non-Pharmacological
- Weight loss
- Physical therapy
- Exercise
- Heat or cold therapy
- Joint protection – Aids/appliances
Pharmacological
- Symptom modifying
- Acetaminiphen
- NSAIDs
- Non selective
- COX II selective
- Other analgesics-opoids
- Structure modifying
- Glucosamine
- Chondroitin sulfate
- Diacerin
- Fatty acids
- Viscosupplementation
- Hyaluronic acid
Surgical management
- Arthroscopy
- Joint replacement
- Cartilage transplantation
